New PyLoose Linux malware mines crypto directly from memory
A new fileless malware named PyLoose has been targeting cloud workloads to hijack their computational resources for Monero cryptocurrency mining.
PyLoose is a relatively simple Python script with a precompiled, base64-encoded XMRig miner, a widely abused open-source tool that uses CPU power to solve complex algorithms required for cryptomining.
According to researchers at Wiz, PyLoose's direct execution from memory makes it incredibly stealthy and challenging to detect by security tools.
Fileless malware leaves no physical footprint on the system's drives, so it's less vulnerable to signature-based detection and typically utilizes legitimate system tools (living off the land) to inject malicious code into legitimate processes.
Wiz's security researchers first detected PyLoose attacks in the wild on June 22nd, 2023, and have since confirmed at least 200 cases of compromise by the novel malware.
"As far as we know, this is the first publicly documented Python-based fileless attack targeting cloud workloads in the wild, and our evidence shows close to 200 instances where this attack was used for cryptomining," explains the new Wiz report.
PyLoose attack chain
Wiz observed attacks that began by gaining initial access to devices through publicly accessible Jupyter Notebook services, which failed to restrict system commands.
The attacker uses an HTTPS GET request to fetch the fileless payload (PyLoose) from a Pastebin-like site, "paste.c-net.org," and load it straight into Python's runtime memory.
The PyLoose script is decoded and decompressed, loading a precompiled XMRig miner directly into the instance's memory using the "memfd" Linux utility, a known fileless malware technique in Linux.
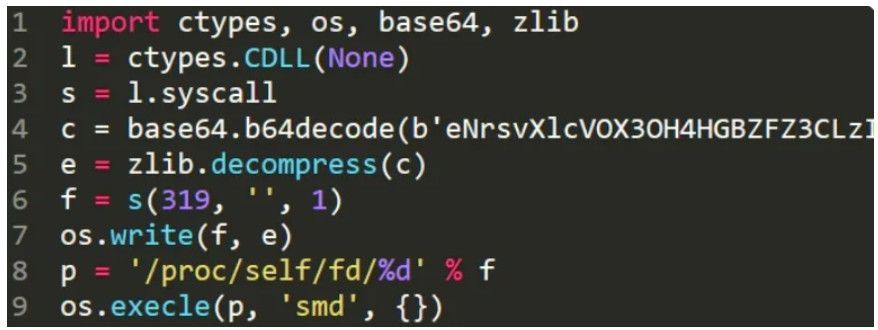
The PyLoose script (Wiz)
"The memory file descriptor, memfd, is a Linux feature that allows the creation of anonymous memory-backed file objects that can be used for various purposes, such as inter-process communication or temporary storage," explains Wiz in the report.
"Once the payload is placed within a memory section created via memfd, attackers can invoke one of the exec syscalls on that memory content, treating it as if it were a regular file on disk, and thereby launch a new process."
This enables attackers to perform payload execution straight from memory, evading most traditional security solutions.
The XMRig miner loaded into the compromised cloud instance's memory is a fairly recent version (v6.19.3) that uses the 'MoneroOcean' mining pool to mine for Monero.
Unknown threat actors
Wiz could not attribute the PyLoose attacks to any particular threat actor, as the attacker left no useful evidence behind.
The researchers comment that the adversary behind PyLoose appears highly sophisticated and stands out from the typical threat actors engaging in cloud workload attacks.
Cloud instance administrators are recommended to avoid the public exposure of services susceptible to code execution, use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to protect access to those services, and place system command execution restrictions.
Source: bleepingcomputer.com
Bạn cũng có thể quan tâm
All Rights Reserved | John&Partners LLC.






