45k Jenkins servers exposed to RCE attacks using public exploits
Researchers found roughly 45,000 Jenkins instances exposed online that are vulnerable to CVE-2023-23897, a critical remote code execution (RCE) flaw for which multiple public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits are in circulation.
Jenkins is a leading open-source automation server for CI/CD, allowing developers to streamline the building, testing, and deployment processes. It features extensive plugin support and serves organizations of various missions and sizes.
On January 24, 2024, the project released versions 2.442 and LTS 2.426.3 to fix CVE-2023-23897, an arbitrary file read problem that can lead to executing arbitrary command-line interface (CLI) commands.
The issue arises from the CLI's feature that automatically replaces an @ character followed by a file path with the contents of the file, a functionality intended to facilitate command argument parsing.
However, this feature, enabled by default, allows attackers to read arbitrary files on the Jenkins controller's file system.
Depending on their level of permissions, attackers can exploit the flaw to access sensitive information, including the first few lines of any file or even entire files.
As the software vendor described in the relevant security bulletin, CVE-2023-23897 exposes unpatched instances to several potential attacks, including RCE, by manipulating Resource Root URLs, "Remember me" cookies, or CSRF protection bypass.
Depending on the instance's configuration, attackers could decrypt stored secrets, delete items from Jenkins servers, and download Java heap dumps.
Late last two week, security researchers warned of multiple working exploits for CVE-2023-23897, which dramatically elevates the risk for unpatched Jenkins servers and increases the likelihood of in-the-wild exploitation.
Researchers monitoring Jenkins honeypots observed activities that resemble genuine attempts at exploitation, although there's no conclusive evidence yet.
On January 29, threat monitoring service Shadowserver reported that its scanners have "caught" roughly 45,000 unpatched Jenkins instances, indicating a massive attack surface.
Most of the vulnerable internet-exposed instances are in China (12,000) and the United States (11,830), followed by Germany (3,060), India (2,681), France (1,431), and the UK (1,029).
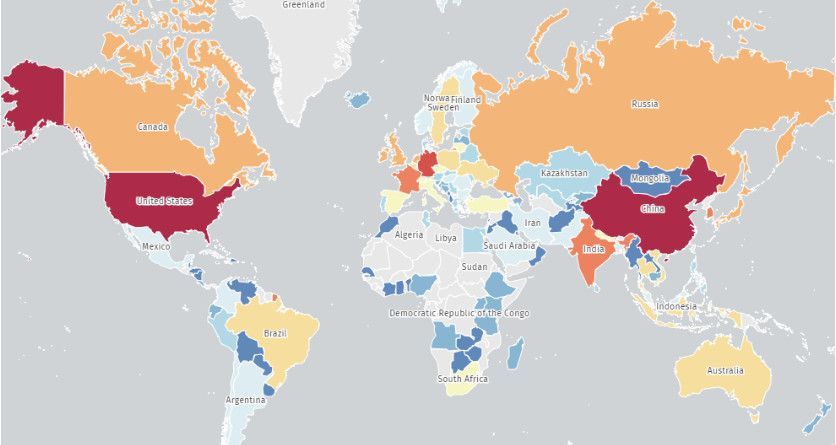
Vulnerable instances exposure heatmap (ShadowServer)
Shadowserver's stats represent a dire warning to Jenkins administrators, as hackers are very likely already conducting scans to find potential targets, and CVE-2023-23897 can have severe repercussions if successfully exploited.
Users unable to apply the available security updates immediately should consult the Jenkins security bulletin for mitigation recommendations and potential workarounds.
Source: bleepingcomputer.com
Bạn cũng có thể quan tâm
All Rights Reserved | John&Partners LLC.






